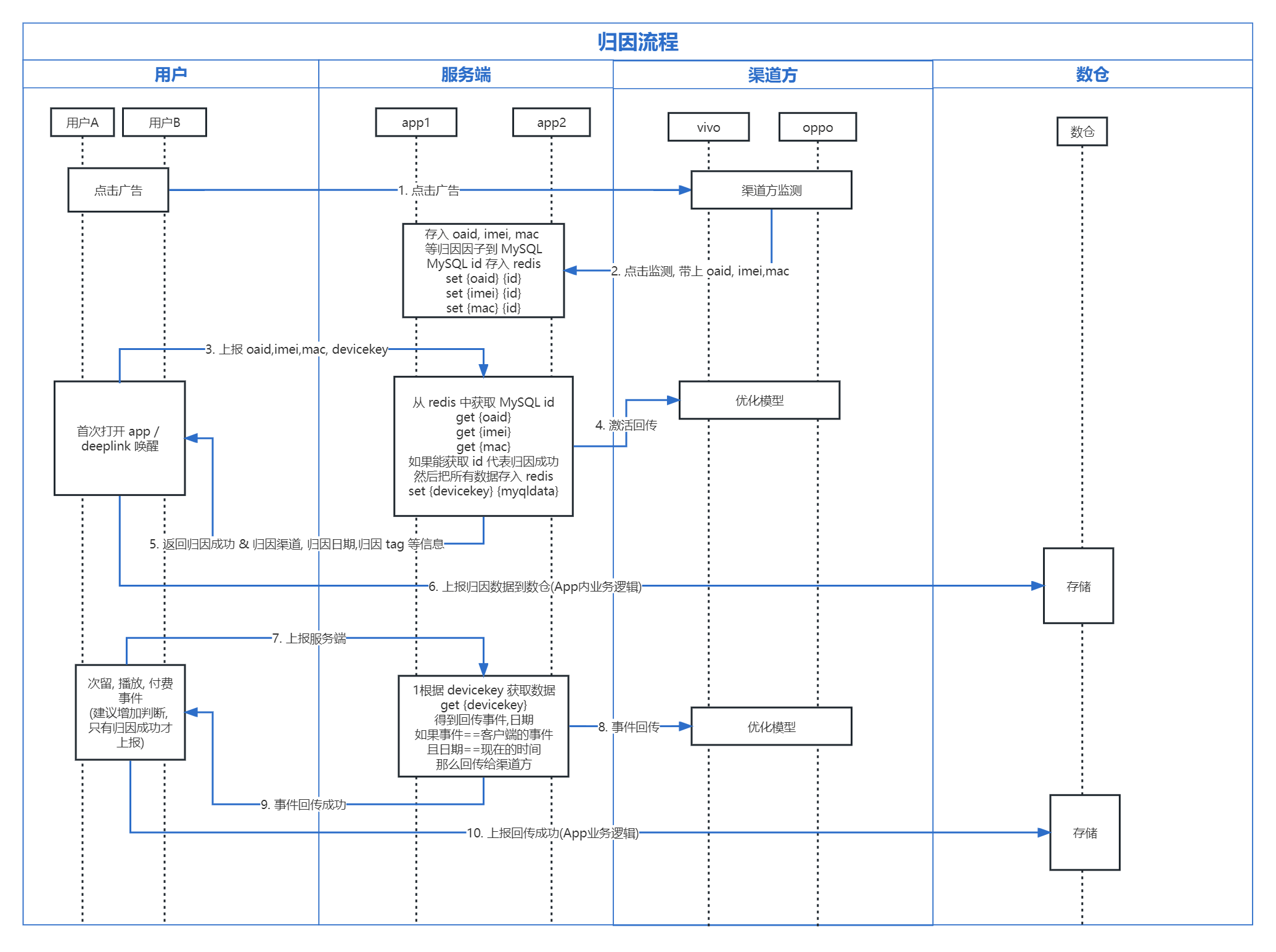
Explanation
- Many concepts in this article reference insights from Sensors Data documentation.
Attribution Methods
-
Self-Attribution
- Tracked by ad platforms. Some platforms receive app-open callbacks from users and perform attribution internally.
- Others like Huawei store attribution data locally during app installation, retrievable during first launch.
-
Impression Attribution
- Rarely used due to massive data volumes.
-
Click Attribution (Most Common)
- Attributes conversions to the last ad click before conversion.
Attribution Models
-
Last-Touch Model (Most Common)
- 100% credit to the final touchpoint before conversion.
-
First-Touch Model
- 100% credit to the initial touchpoint that introduced the user.
-
Linear Model
- Equal credit distribution across all touchpoints.
-
Time-Decay Model
- Higher weight given to more recent interactions.
-
Position-Based Model
- 40% credit to first/last touchpoints, 20% distributed among others.
-
Custom Weighted Model
- Custom weights assigned to different channels.
Matching Methods
-
Exact Matching
- Uses device identifiers:
OAID,AndroidID,IMEI,MAC.
- Uses device identifiers:
-
Fuzzy Matching
- Uses
IPaddresses andUser-Agentstrings.
- Uses
Architecture Implementation
Core Database Schema
-- Applications Table (apps)
id, appid, name, os, attribute_cycle_days, attribute_white_list(JSON)
-- Channels Table (channels)
id, name, template_query
-- Tracking Links Table (links)
id, app_id, channel_id, channel_name, events(JSON), exp
-- Click Logs Table (click_logs, daily partitioned)
id, appid, ad_name, oaid, imei, android_id, mac, ip, ua, exp, callback, data(JSON), attributed_at
-- Attribution Logs & Callback Logs (custom logging)
Key Workflows
1. Ad Click Tracking (Endpoint)
// Unified request structure
class AdClickRequest {
public $oaid;
public $imei;
public $imei_md5;
public $android_md5;
public $ad_name;
public $callback;
}
// Simplified endpoint logic
function clickLogs($id) {
// 1. Parse request
$req = new AdClickRequest(/* input params */);
// 2. Validate tracking link
$link = DB::table('links')->find($id);
if (!$link) return response('FAIL', 400);
// 3. Insert click log (async via queue)
$log = ClickLog::create([
'oaid' => $req->oaid,
'imei' => $req->imei_md5,
'events' => $link->events,
'exp' => $link->exp
]);
// 4. Cache identifiers for attribution window
Redis::pipeline(function($pipe) use ($link, $req) {
foreach (['oaid','imei_md5','android_md5'] as $field) {
$key = "attr:{$link->app_id}_{$req->$field}";
$pipe->setex($key, $link->exp*86400, "{$log->id}:{$log->table}");
}
});
return response('OK');
}
2. First Launch Attribution
class AppReportRequest {
public $device_key;
public $oaid;
public $imei;
public $mac;
}
function appReport($appId) {
// 1. Parse device data
$req = new AppReportRequest(/* input */);
// 2. Check cached click logs
$matchedLog = null;
foreach (['oaid','imei','mac'] as $field) {
$key = "attr:{$appId}_{$req->$field}";
$logInfo = Redis::get($key);
if ($logInfo) {
[$logId, $table] = explode(':', $logInfo);
$matchedLog = DB::table($table)->find($logId);
break;
}
}
if (!$matchedLog) return response('No attribution', 404);
// 3. Record attribution
Redis::setex("attr_device:{$appId}_{$req->device_key}", 604800, $matchedLog->id);
// 4. Cleanup & async callbacks
Redis::del(array_keys($matchedKeys));
Queue::dispatch(new ProcessAttribution($matchedLog));
return response('OK');
}
3. Event Callbacks
function eventCallback($appId, $event, $deviceKey) {
$logId = Redis::get("attr_device:{$appId}_{$deviceKey}");
$log = ClickLog::find($logId);
// Validate event against link configuration
if (in_array($event, json_decode($log->events))) {
// Execute channel-specific callback template
Http::post($log->callback, [
'event' => $event,
'params' => $log->data
]);
}
return response('Processed');
}
Debugging Tools
1. Device Attribution Checker
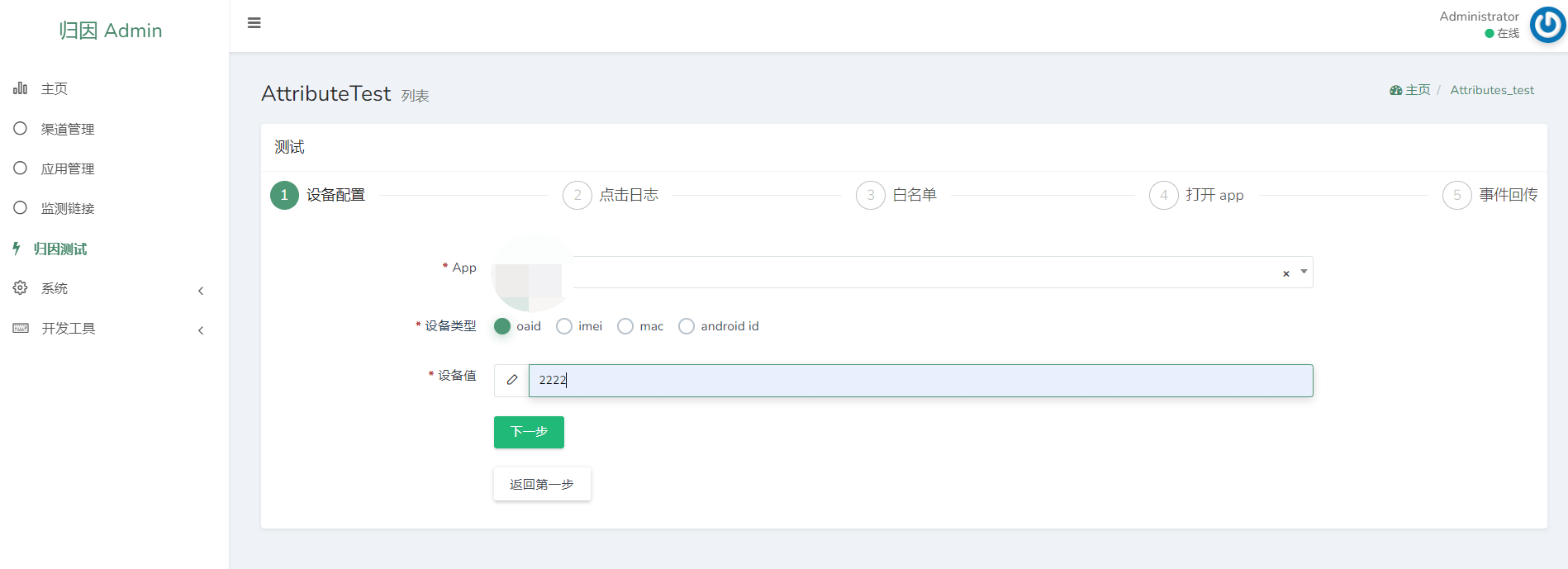
Input device identifiers to simulate attribution matching.
2. Real-time Click Log Monitoring
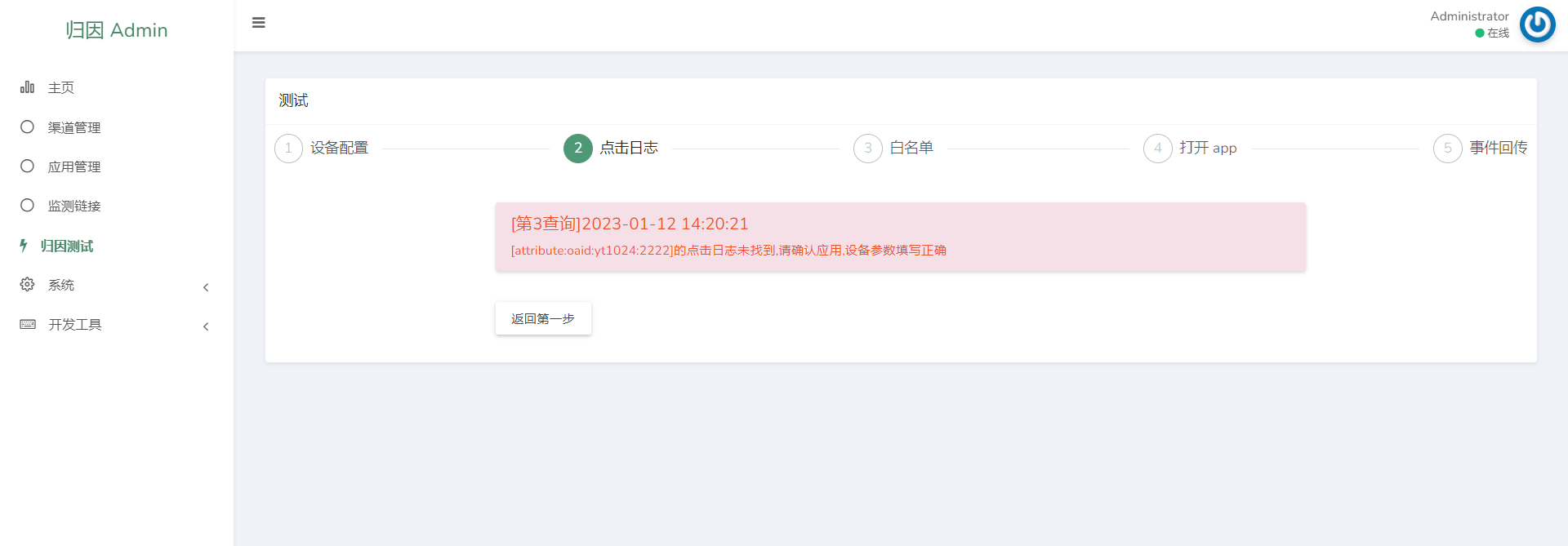
Verify if click logs are received from ad platforms.
3. Attribution Whitelisting
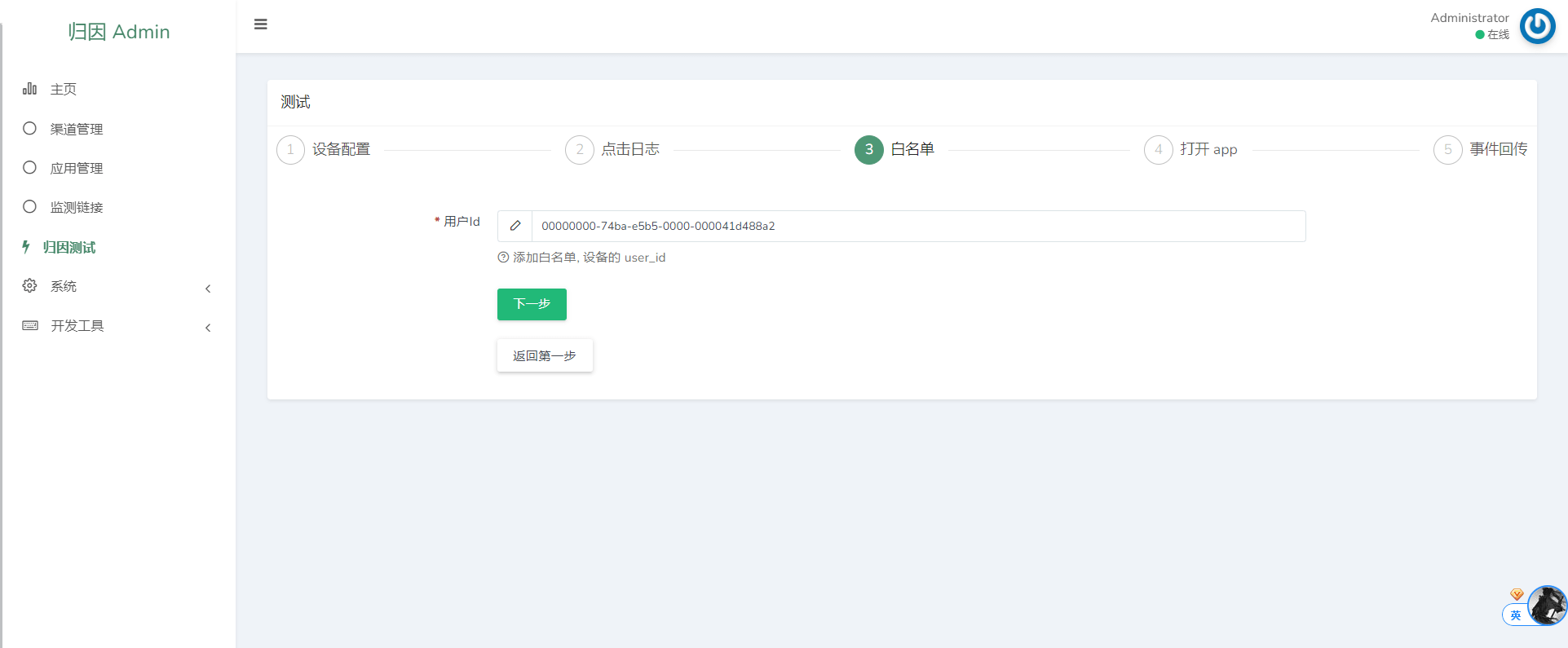
Bypass attribution rules for testing specific devices.
4. Event Callback Testing
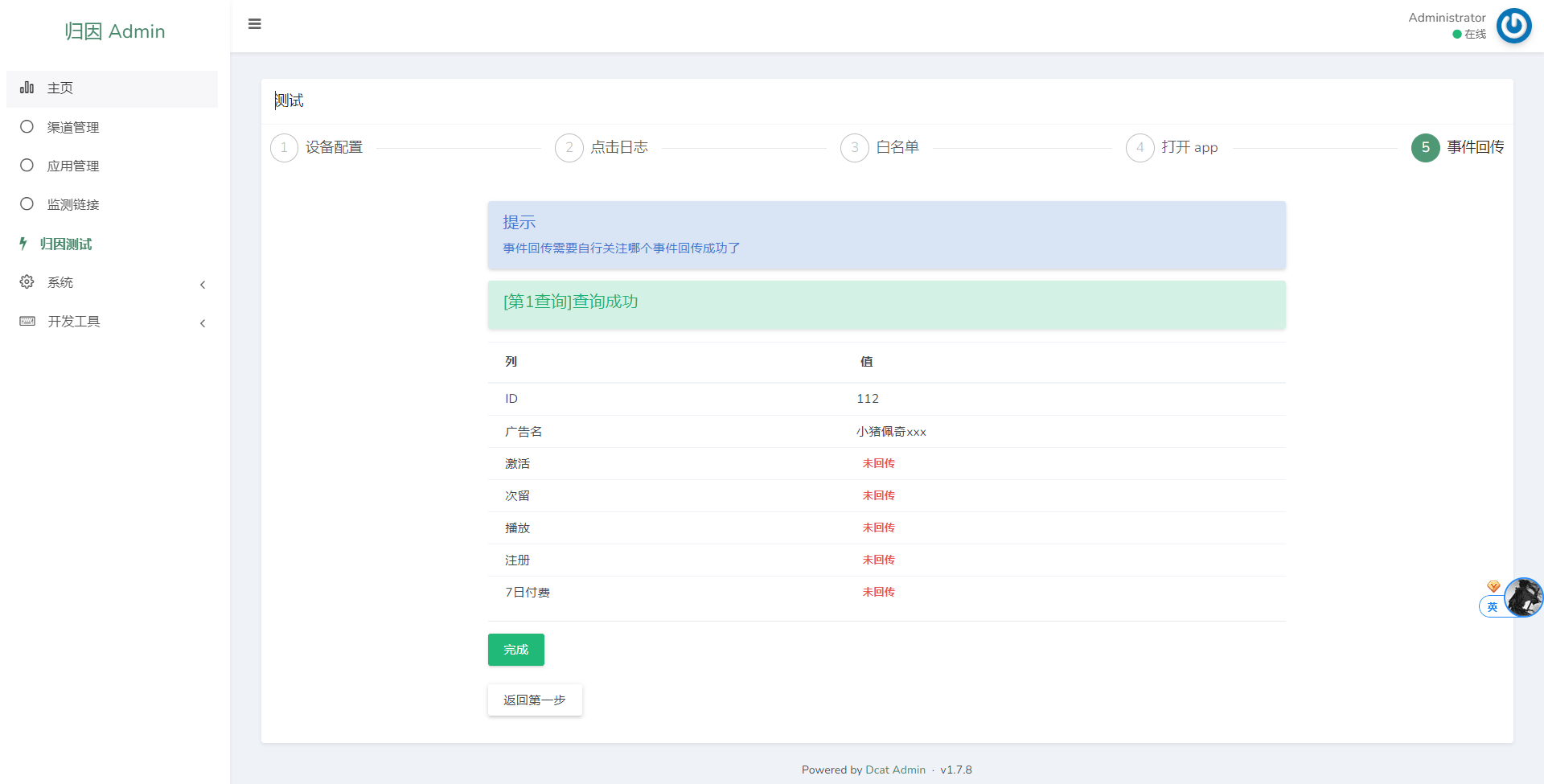
Manually trigger and verify postback events.
Client Implementation
// Unified attribution handler
class AttributionTracker {
constructor() {
this.storageKey = 'attribution_events';
}
track(event) {
const sentEvents = this._getSentEvents();
if (sentEvents[event]) return;
api.post('/callback', { event }).then(() => {
sentEvents[event] = true;
this._saveEvents(sentEvents);
});
}
attributeLaunch() {
api.post('/launch').then(() => {
this._clearSentEvents();
});
}
_getSentEvents() {
return JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem(this.storageKey)) || {};
}
_saveEvents(events) {
localStorage.setItem(this.storageKey, JSON.stringify(events));
}
_clearSentEvents() {
localStorage.removeItem(this.storageKey);
}
}
This architecture provides:
- Modular Design: Separates click tracking, attribution matching, and callback execution.
- Scalable Storage: Uses partitioned tables and Redis for high-frequency operations.
- Flexible Matching: Supports both exact and fuzzy matching strategies.
- Debuggability: Comprehensive tools for platform verification and testing.