- Following the previous Redis incident, our monitoring system recently alerted about abnormal MySQL load in the advertising system
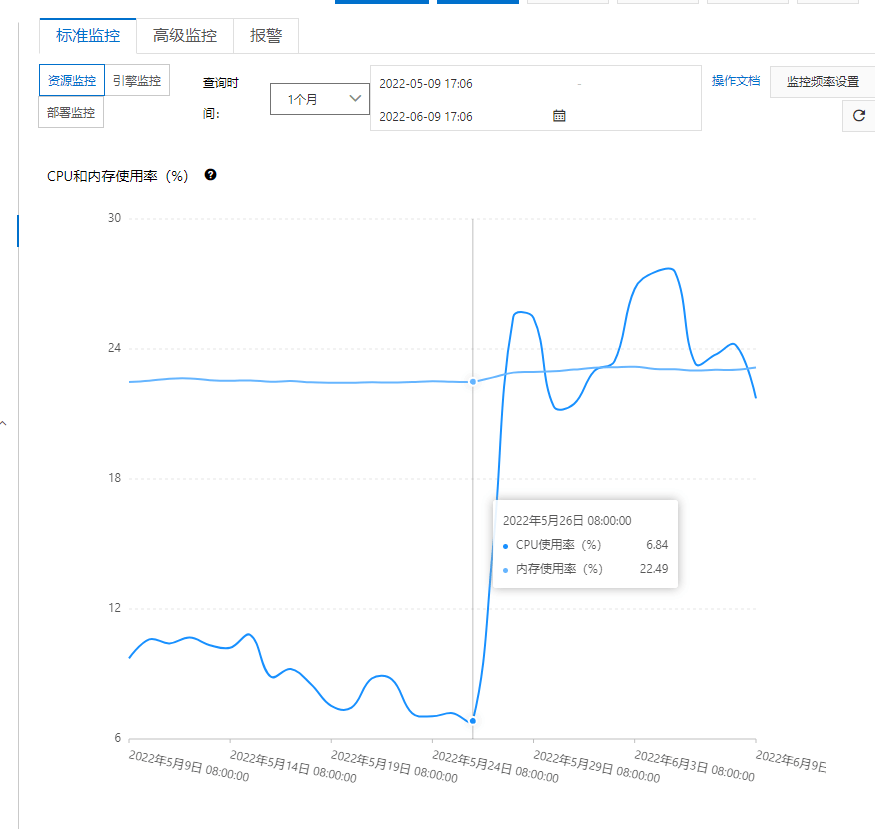
- The Ops team asked me to investigate whether recent code changes caused the database load spike. As shown:
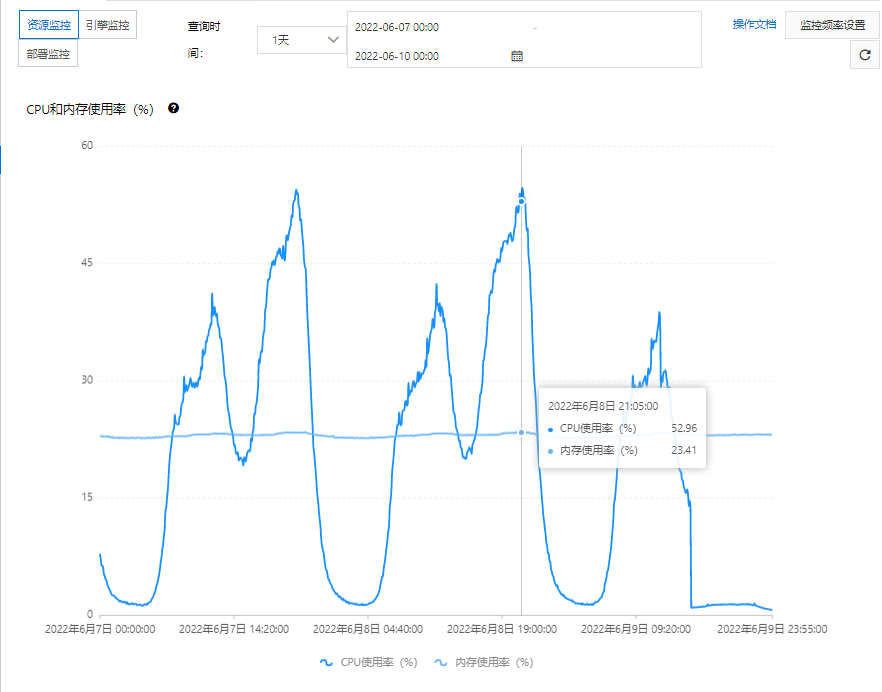
- The graph clearly shows a sudden load surge at the marked timestamp, which persisted without subsiding
- Checking Git commit history revealed no deployments on that day, indicating operational configuration changes might be the culprit
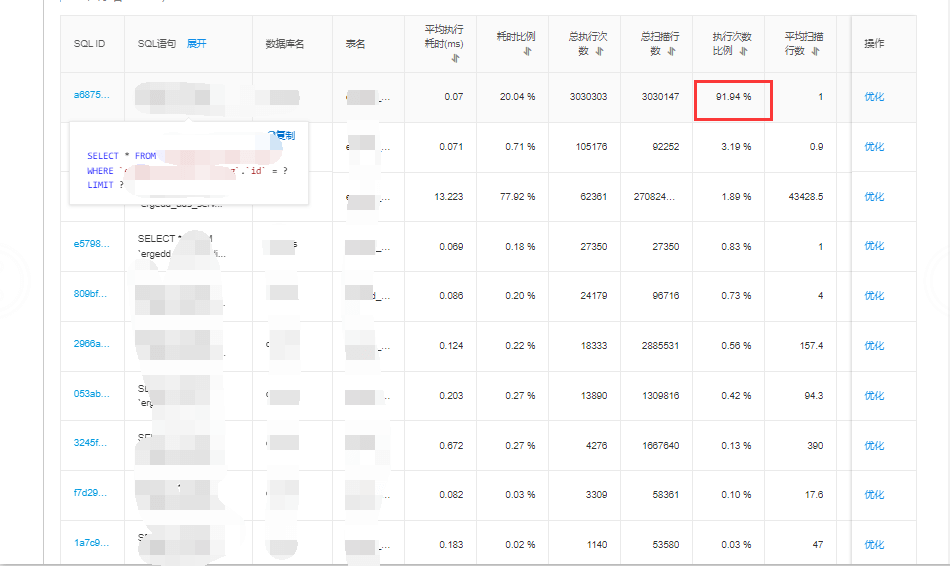
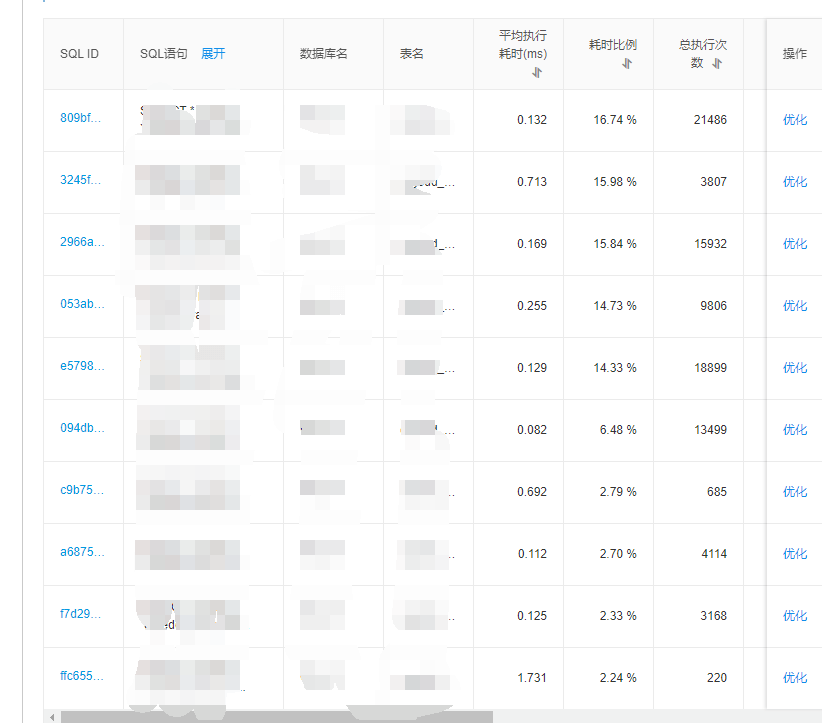
- Accessed Alibaba Cloud’s SQL Audit and Analysis feature (similar solutions exist on other cloud platforms):
- The problematic SQL query was quickly identified, accounting for over 90% of total queries
- Next steps were straightforward:
- Locate the corresponding code for this SQL
- Root cause analysis:
- Original code handled single configurations, but recent operational changes allowed multiple options
- No caching implementation
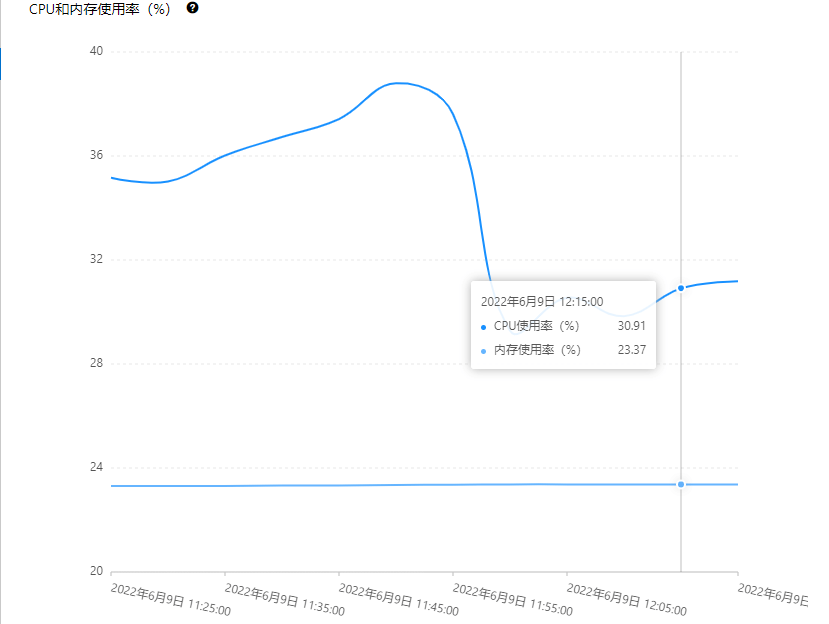
- Optimized query logic and added caching mechanisms
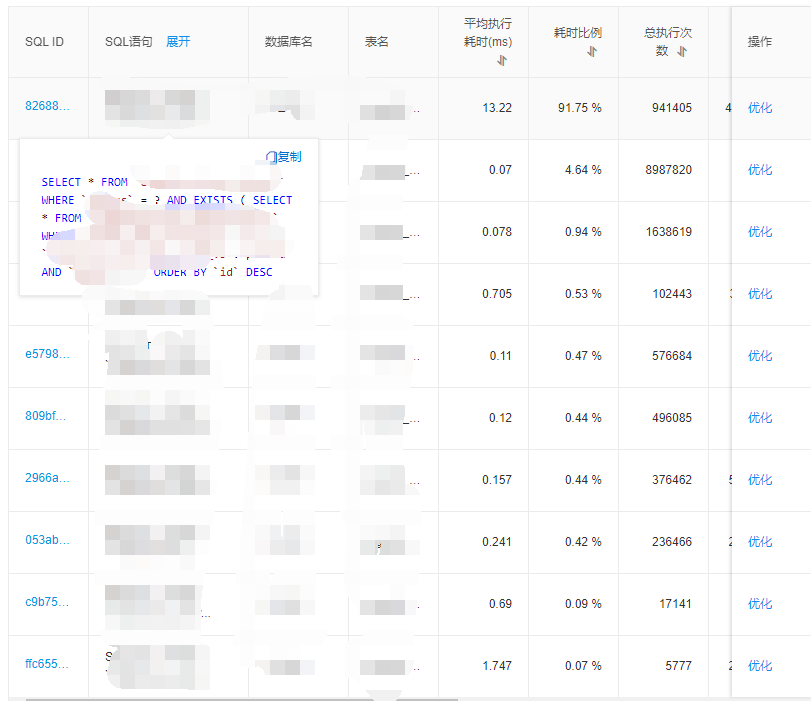
- Post-optimization showed reduced database load, but another SQL query became prominent with higher average latency due to
WHERE EXISTSusage:- The Laravel
whereHasmethod generated inefficientWHERE EXISTSqueries - GitHub solutions suggested using
WHERE INinstead - Implemented custom solution using these patterns (alternative packages available):
- The Laravel
- Final optimizations resulted in:
- Balanced query distribution
- Database load reduced to 1% (compared to ~50% previously)
- Consistent performance during peak periods