Recently encountered a linked list reversal problem on LeetCode:
Reverse a singly linked list.
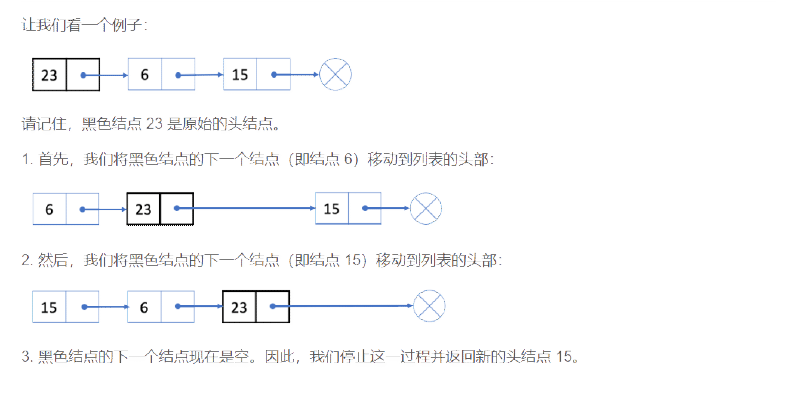
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Iterative Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode *tmpHead = head, *nextNode;
if (NULL == head) {
return head;
}
while (NULL != head->next) {
// Move the next node of current 'head' to real head position
nextNode = head->next;
head->next = head->next->next;
nextNode->next = tmpHead;
tmpHead = nextNode;
}
return tmpHead;
}
Recursive Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if (NULL == head) {
return NULL;
}
else if (NULL == head->next) {
return head;
}
struct ListNode *currNode = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return currNode;
}
/* Execution process:
reverseList([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) {
reverseList([2, 3, 4, 5]) {
reverseList([3, 4, 5]) {
reverseList([4, 5]) {
reverseList([5]) {
// 1. Here next is NULL, return current node
return 5;
}
// 2. Make 5 point to 4, set 4's next to NULL
[4, 5]->next->next = [4, 5];
[4, 5]->next = NULL;
return [5, 4];
}
// 3. Make 4 point to 3, set 3's next to NULL
[3, 4]->next->next = [3, 4];
[3, 4]->next = NULL;
return [5, 4, 3];
}
// 4. Make 3 point to 2, set 2's next to NULL
[2, 3]->next->next = [2, 3];
[2, 3]->next = NULL;
return [5, 4, 3, 2];
}
// 5. Make 2 point to 1, set 1's next to NULL
[1, 2]->next->next = [1, 2];
[1, 2]->next = NULL;
return [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
}
*/
Key points:
- Recursive approach uses the call stack to process nodes from end to start
- Each recursion level handles the pointer redirection:
head->next->next = headmakes next node point to current nodehead->next = NULLbreaks the original link
- The deepest recursion returns the new head (original tail node) which propagates back through all recursion levels